Table of Contents
Introduction
Exploring the French-speaking countries in Africa is a journey into a rich tapestry of history, culture, and global influence. Africa, with its diverse nations and vibrant cultures, has a unique relationship with the French language. This relationship is rooted in colonial history, yet it continues to evolve in the modern era, shaping the continent's identity and its role on the global stage.
French is one of the most widely spoken languages in Africa, second only to Arabic and English. It serves as a lingua franca in many regions, facilitating communication, trade, and diplomacy. The presence of French in Africa is not just a relic of the past; it is a living, dynamic force that influences education, politics, and culture across the continent.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of French-speaking African countries. From their historical ties with France to their current contributions to the global Francophone community, we will explore the significance of these nations. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the role French plays in Africa and why it matters in today's interconnected world.
Read also:Deiondra Sanders A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Achievements And Influence
History of French in Africa
The roots of the French language in Africa can be traced back to the colonial era, when France established its presence across the continent. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, France colonized vast territories in West and Central Africa, imposing its language and culture on the local populations. This period of colonization laid the foundation for the widespread use of French in Africa today.
After gaining independence in the mid-20th century, many African nations chose to retain French as an official language. This decision was driven by practical considerations, such as the need for a common language to unite diverse ethnic groups, as well as the desire to maintain economic and diplomatic ties with France. Over time, French evolved from a colonial imposition to a tool of empowerment and global connection.
Today, the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie (OIF) plays a key role in promoting the French language and fostering cooperation among French-speaking nations. Africa is home to the largest number of French speakers globally, and the continent's influence within the Francophone community continues to grow.
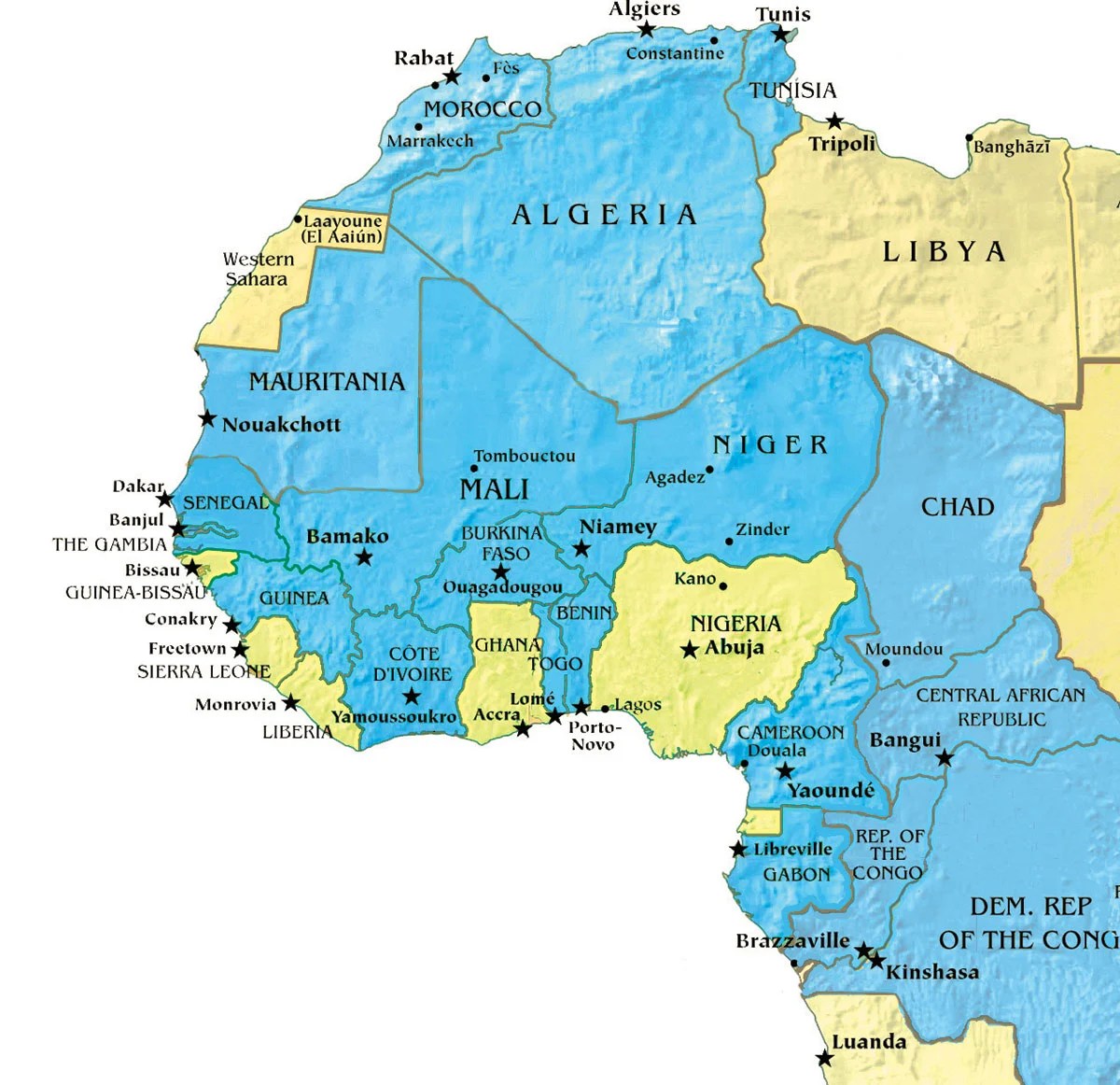
List of French-Speaking Countries in Africa
Africa is home to 29 countries where French is an official language. These nations span across West, Central, and North Africa, forming a significant part of the global Francophone community. Below is a list of these countries, along with a brief overview of their linguistic and cultural significance.
West Africa
- Senegal: Known for its vibrant music and arts scene, Senegal is a cultural hub in West Africa.
- Ivory Coast: A major economic powerhouse in the region, with French as the primary language of business.
- Mali: French is widely used in education and governance.
- Guinea: French serves as a unifying language among diverse ethnic groups.
- Niger: French is essential for communication in this landlocked nation.
Central Africa
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC): The most populous French-speaking country in the world.
- Cameroon: A bilingual nation with both French and English as official languages.
- Gabon: French dominates in government, education, and media.
- Chad: French is used alongside Arabic as an official language.
- Central African Republic: French is a key language for administration and education.
North Africa
- Tunisia: French remains influential in business and education.
- Morocco: French coexists with Arabic as a dominant language.
- Algeria: French is widely spoken despite the country's Arabization policies.
These countries, along with others like Burkina Faso, Benin, and Madagascar, form a vibrant network of French-speaking nations that contribute to the global Francophone community.
Cultural Influence of French in Africa
The French language has had a profound impact on African culture, influencing everything from literature and music to cinema and cuisine. African writers such as Chinua Achebe and Ngũgĩ wa Thiong'o have often written in French, contributing to a rich tradition of Francophone literature. Similarly, African musicians like Youssou N'Dour and Angelique Kidjo have used French to reach global audiences.
Read also:Star Shaped Perfume Bottle The Ultimate Guide To Beauty And Functionality
Film festivals and cultural events celebrating the French language are held regularly across the continent. These events not only showcase African talent but also strengthen ties between African nations and the broader Francophone world. French has become a medium for expressing African identity and creativity on the global stage.
In addition to the arts, French has influenced African cuisine and fashion. French culinary techniques and ingredients have been adapted to local tastes, resulting in unique fusion dishes. Similarly, French fashion trends have been embraced and reinterpreted by African designers, creating a distinct style that reflects the continent's diversity.
Economic Significance of French-Speaking Countries
The French-speaking countries in Africa are not only culturally rich but also economically significant. Many of these nations are key players in industries such as mining, agriculture, and energy. For example, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a leading producer of cobalt, while Ivory Coast is a major exporter of cocoa.
French serves as a bridge for international trade and investment in these countries. It facilitates communication between African businesses and their French counterparts, as well as other Francophone nations. This linguistic connection has helped foster economic partnerships and development projects across the continent.
Furthermore, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) has highlighted the importance of French as a language of commerce. With many African countries participating in this initiative, French-speaking nations are well-positioned to benefit from increased trade and collaboration within the region.
Education and the French Language
Education is a critical area where the influence of French is most evident. In many African countries, French is the primary language of instruction in schools and universities. This has created a generation of French-speaking professionals who are equipped to compete in the global job market.
However, the dominance of French in education has also sparked debates about language policy. Some argue that the emphasis on French marginalizes indigenous languages and limits access to education for rural communities. Efforts are being made to promote bilingual education and preserve local languages while maintaining the benefits of French proficiency.
International organizations like UNESCO and the OIF are working to improve educational opportunities in French-speaking African countries. These initiatives aim to enhance literacy rates, promote gender equality, and ensure that all children have access to quality education in their native languages as well as French.
French in African Politics
French plays a crucial role in African politics, serving as a medium for diplomacy, governance, and international relations. Many African leaders are fluent in French, enabling them to engage with their counterparts in France and other Francophone nations. This linguistic connection has facilitated cooperation on issues such as climate change, security, and development.
The influence of France in African politics remains a topic of discussion. While some view France's involvement as a continuation of colonial ties, others see it as a partnership that benefits both parties. French-speaking African countries often collaborate with France on economic and military initiatives, highlighting the enduring impact of their shared history.
At the same time, there is a growing movement toward greater autonomy and self-determination among African nations. This has led to calls for diversifying language use in politics and reducing reliance on French. Despite these challenges, French remains an important tool for fostering unity and collaboration within the African Union and beyond.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the French language offers numerous opportunities for African nations, it also presents certain challenges. One of the main issues is the tension between preserving indigenous languages and promoting French as a global language. Balancing these priorities is essential for ensuring that all communities have access to education and economic opportunities.
Another challenge is the perception of French as a colonial legacy. Some critics argue that the continued use of French perpetuates inequalities and reinforces power dynamics established during the colonial era. Addressing these concerns requires a nuanced approach that acknowledges the historical context while embracing the potential of French as a unifying force.
Despite these challenges, there are significant opportunities for growth and innovation. The rise of digital technology has created new platforms for promoting the French language and culture in Africa. Social media, online education, and digital content creation are empowering young Africans to engage with the global Francophone community in unprecedented ways.
Future of French in Africa
The future of French in Africa is bright, with the continent poised to become the epicenter of the global Francophone community. By 2050, it is estimated that 85% of the world's French speakers will reside in Africa, reflecting the continent's demographic growth and linguistic dynamism.
Efforts to promote multilingualism and cultural exchange will play a key role in shaping the future of French in Africa. Initiatives such as the OIF's "Francophonie" program aim to strengthen ties between French-speaking nations while celebrating their diversity. These efforts will ensure that French remains a vibrant and relevant language in the 21st century.
At the same time, African nations are redefining their relationship with French, using it as a tool for empowerment and global engagement. Whether in education, business, or diplomacy, French will continue to be a vital part of Africa's identity and its contributions to the world.
Conclusion
Exploring the French-speaking countries in Africa reveals a fascinating blend of history, culture, and global influence. From its colonial roots to its modern-day significance, French has become an integral part of the continent's identity. It serves as a bridge for communication, trade, and cultural exchange, connecting African nations with each other and the wider world.
As we have seen, the role of French in Africa is multifaceted, encompassing education, politics, economics, and culture. While challenges remain, the opportunities for growth and innovation are immense. By embracing multilingualism and fostering collaboration, African nations can harness the power of French to build a brighter future for their people.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this topic in the comments below. Have you visited any French-speaking African countries? How do you think the French language will continue to evolve in Africa? Don't forget to share this article with others who might find it interesting, and explore more of our content to learn about the diverse cultures and languages of the world.